How to Use Technographic Segmentation for Better Marketing

Table of Contents
To market effectively, you need to know more than just who your audience is—you need to understand the technology they use. Technographic segmentation helps businesses group customers based on the tools, software, and platforms they rely on. This allows marketers to create more relevant messaging, personalize outreach, and improve ad targeting.
In this guide, we’ll break down how technographic segmentation works and how you can use it to make your marketing smarter and more effective.
Why Is Technographic Segmentation Important?
Technographic segmentation is a marketing strategy that categorizes customers based on their technology usage, preferences, and behaviors. This approach focuses specifically on how individuals and organizations interact with various technologies, and it divides your market into segments based on technology adoption patterns.
The method examines several components:
- Device types used (smartphones, tablets, laptops)
- Operating systems and software preferences
- Application and tool usage (such as CRM or marketing automation tools)
- Cloud service adoption patterns
- Social media and e-commerce activities
- Technology spending behaviors
- Attitudes towards new technologies
Technographic segmentation helps with several marketing goals:
- It identifies prospects with compatible technology stacks.
- It reveals opportunities to address integration needs or technology gaps.
- It enables more relevant messaging that speaks to a prospect’s technical environment.
- It improves lead qualification by focusing on companies with the right technological fit.
- It provides insights into market trends and technology adoption patterns.
The Benefits of Technographic Segmentation
Technographic segmentation uses data to provide deeper insights into how prospects interact with technology, leading to various benefits:
1. Laser-Focused Targeting
By understanding the technology stack of potential customers, you can create distinct segments based on:
- Device types used
- Operating systems and software applications
- Cloud services adoption
- Social media platform usage
- E-commerce behaviors
This granular segmentation allows you to tailor messaging that aligns with the technology preferences of each segment.
2. Hyper-Personalized Marketing
Technographic segmentation enables personalization beyond basic demographic targeting. When you know which technologies your prospects use, you can create messages that speak to their specific situation.
By leveraging technographic data, you can:
- Customize content formats based on preferred devices
- Tailor product demos to match technical proficiency levels
- Address specific integration challenges with existing technology
- Highlight features that complement tools already in use
This personalization builds stronger relationships by showing you understand each prospect’s technological environment.
3. Higher Conversion Rates and Shorter Sales Cycles
Technographic segmentation delivers better conversion rates and shorter sales cycles thanks to its ability to:
- Qualify leads more effectively based on technological fit
- Create more relevant messaging that resonates immediately
- Identify integration opportunities that speed up implementation
- Focus sales efforts on prospects with compatible technology stacks
4. Optimized Marketing Spend
By targeting prospects based on their technology usage, you can allocate your marketing budget more efficiently. This approach reduces wasted spend on prospects who are poor technological fits for your product.
Companies that implement technographic segmentation often reallocate their budget from least to most effective media channels based on technology-specific performance data. This process typically involves:
- Gathering data on how different technology segments respond to various marketing channels
- Implementing dynamic budget allocation based on real-time performance
- Conducting ongoing A/B tests for different technographic segments
- Making data-driven adjustments to spending levels based on results
Key Technographic Data Points to Consider
When implementing technographic segmentation, focus on specific data points that reveal how target companies use technology. These elements help you craft more targeted campaigns and better position your solutions.
Technology Stack and Software Versions
The technology stack is a fundamental starting point for technographic analysis. Investigate:
- Operating systems: Identify which OS types your targets use, including specific versions. This reveals compatibility requirements and potential upgrade opportunities.
- Web browsers: Track which browsers your prospects prefer, along with version numbers. Browser choices can indicate technical preferences and security considerations.
- Programming languages: Look at primary languages and frameworks that companies employ. This reveals their development approach and potential integration requirements.
- Databases: Determine whether companies use SQL or NoSQL solutions and whether they’ve adopted cloud or on-premises deployments.
- Software applications: Examine their CRM, marketing automation platforms, CMS solutions, and analytics tools. The specific edition reveals budget priorities and technical sophistication.
- Version information: Assess whether prospects maintain current software versions or rely on legacy systems, which indicates their innovation appetite.
- Cloud adoption: Evaluate their usage of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS solutions, which demonstrates digital transformation progress.
Adoption Patterns and Integration Needs
Four key factors influence technology adoption :
- Performance expectancy: The degree to which an organization believes a technology will improve performance
- Effort expectancy: The perceived ease of use associated with the technology
- Social influence: How industry peers view the technology
- Facilitating conditions: The organizational and technical infrastructure needed to support implementation
By examining these factors, you can address specific adoption barriers your prospects face.
Want to test drive Metadata?
How to Apply Technographic Segmentation in Your Marketing Strategy
Implementing technographic segmentation transforms your marketing efforts by leveraging insights about your prospects’ technology usage.
Lead Scoring and Prioritization
Technographic data is invaluable for lead scoring and prioritization as well as broader demand generation strategies.
To implement technographic lead scoring:
- Gather technographic data: Use specialized data providers like HG Insights, Clearbit, or BuiltWith to collect information about technology usage.
- Define scoring criteria: Assign point values to different technologies based on how they correlate with your ideal customer profile.
- Integrate with your existing systems: Sync your technographic data with your CRM or marketing automation platform.
- Create lead tiers: Segment your leads into groups based on their scores.
- Refine and optimize: Regularly analyze conversion rates by score and adjust your model.
Here’s an example of a lead scoring model using technographic data:
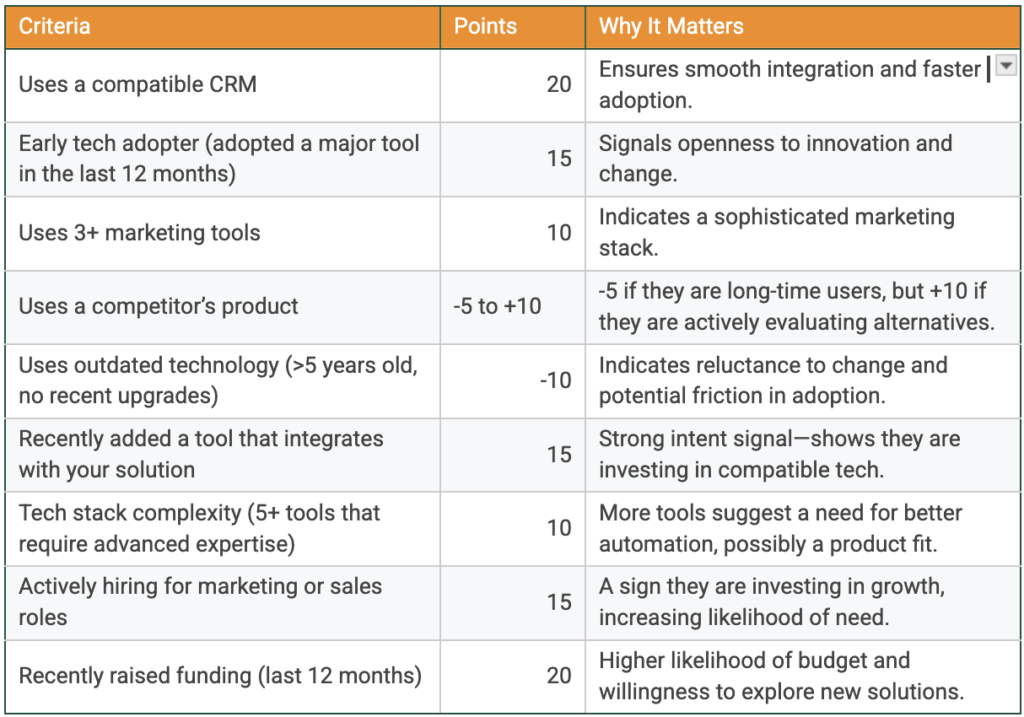
For the best results, combine technographic data with other scoring factors like firmographics and intent data.
Personalized Content and Messaging
When you understand a prospect’s technology environment, you can create content that speaks directly to their specific situation. This personalization improves engagement and conversion rates.
To implement personalized content based on technographic data:
- Create technology-specific content: Develop case studies, integration guides, solution briefs, and repurpose event content for different technology ecosystems.
- Tailor email campaigns: Customize messaging based on the prospect’s current tech stack, addressing specific integration points.
- Dynamic website content: Implement content personalization that adjusts based on the visitor’s detected technology profile.
- Sales enablement materials: Provide your sales team with technology-specific talking points.
The key is making your content relevant to the specific technological context of your prospects. For example, if you know a company uses Salesforce, highlight your product’s Salesforce integration capabilities and showcase success stories from other Salesforce users.
By addressing the specific technical challenges your prospects face, you demonstrate understanding of their environment and position your solution as a natural fit.
Account-Based Marketing (ABM)
Account-based marketing campaigns target and engage specific high-value accounts with personalized campaigns.
Technographic data improves ABM strategies by allowing you to:
- Select target accounts based on their technology profile
- Create tailored content addressing specific technology challenges
- Personalize outreach with technology-specific messaging
- Align sales and marketing around technology-based account insights
For example, if targeting enterprises using Oracle ERP systems, you can develop customized content addressing common Oracle integration challenges and feature success stories from similar Oracle customers.
However, it’s important to be aware of common ABM misconceptions to fully leverage technographic data in your strategies. For example, many B2B marketers believe that starting with a small, loosely defined target account list is the most effective strategy.
In reality, this approach often leads to challenges in generating leads, as it may focus on ‘dream accounts’ without considering their current needs or intent. A more successful ABM strategy involves casting a wider net initially to understand intent, and then personalizing outreach to those who have shown interest.
Paid Advertising and Retargeting
Technographic segmentation improves paid advertising and retargeting campaigns by enabling more precise targeting and messaging.
With technographic data, you can:
- Create technology-specific ad campaigns that address the unique needs of different technology segments
- Target prospects using complementary technologies through platforms that support technographic targeting
- Develop custom audiences based on technology usage for social media advertising and event marketing
- Create more relevant retargeting ads that speak to a prospect’s specific technology environment
For retargeting, you can show ads featuring product integrations relevant to the technologies a prospect uses. This keeps your brand top-of-mind while highlighting the specific value proposition most relevant to their technology stack.
For example, if a prospect uses HubSpot, your retargeting ads could highlight your HubSpot integration capabilities and show testimonials from other HubSpot customers who have implemented your solution.
Challenges and Limitations of Technographic Segmentation
While technographic segmentation offers powerful insights, it comes with several challenges that marketers need to address.
Data Accuracy and Freshness
Many companies struggle to gather comprehensive technographic data, with limited data availability being a primary obstacle. Also, self-reported data may be inaccurate or incomplete.
The rapidly changing technology environment presents another hurdle. New devices, platforms, and tools constantly emerge, causing technographic segments to become outdated.To address these issues, use multiple data sources, implement regular data updates, and combine technographics with other segmentation approaches.
Integration with Existing CRM and Tools
Poorly integrated data creates silos and inefficiencies. Implementation challenges often include: data format inconsistencies between systems, duplicate entries and data conflicts, user adoption resistance, and integration maintenance requirements.
To overcome these challenges, implement gradually with a phased rollout, provide comprehensive training for your team, and establish open communication channels to address issues.
Cost and Resource Constraints
Implementing technographic segmentation requires investments in data, tools, and expertise that may strain marketing budgets.
Common cost constraints include data acquisition expenses, technology implementation and integration costs, analysis and reporting tool investments, and training and staffing resources.
To manage these constraints:
- Start small with a pilot program focused on high-value segments
- Prioritize spending on the most critical technographic data points
- Look for integrated solutions that combine multiple capabilities
- Consider phased implementation that spreads costs over time
- Monitor ROI continually to justify ongoing investments
Keep in mind that resource constraints go beyond financial considerations. For example, limited technical expertise, competing priorities, and time limitations can all impact implementation.
Elevate Your B2B Marketing with Technographic Segmentation
Technographic segmentation enables more precise targeting, personalized messaging, and optimized ad spend. By understanding the technology stacks, preferences, and adoption behaviors of your prospects, you can craft relevant campaigns that resonate with their needs.
And while challenges like data accuracy, integration issues, and resource constraints exist, businesses that invest in the right tools and strategies can overcome these obstacles and drive measurable success.
Metadata’s MetaMatch solution improves your B2B targeting by creating precise, data-driven audiences. And it leads to improved lead qualification and sales efficiency, while addressing challenges such as data accuracy and integration issues.
Book a demo to learn more about Metadata’s platform.